CHILDREN'S DENTAL HEALTH
30+ Years of ExperienceState-of-the-Art TechnologyPersonalized Care
- 30+ Years of Experience- State-Of-The-Art Technology- Personalized Care
Care for Your Child’s Teeth
Pediatric oral care has two main components: preventative care at the pediatric dentist’s office and preventative care at home. Though infant and toddler caries (cavities) and tooth decay have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, a good dental strategy will eradicate the risk of both.
The goal of preventative oral care is to evaluate and preserve the health of the child’s teeth. Beginning at the age of twelve months, the American Dental Association (ADA) recommends that children begin to visit the pediatric dentist for “well baby” checkups. In general, most children should continue to visit the dentist every six months, unless instructed otherwise.
How can a pediatric dentist care for my child’s teeth?
The pediatric dentist examines the teeth for signs of early decay, monitors orthodontic concerns, tracks jaw and tooth development, and provides a good resource for parents. In addition, the pediatric dentist has several tools at hand to further reduce the child’s risk for dental problems, such as topical fluoride and dental sealants.
During a routine visit to the dentist: the child’s mouth will be fully examined; the teeth will be professionally cleaned; topical fluoride might be coated onto the teeth to protect tooth enamel, and any parental concerns can be addressed. The pediatric dentist can demonstrate good brushing and flossing techniques, advise parents on dietary issues, provide strategies for thumb sucking and pacifier cessation, and communicate with the child on his or her level.
When molars emerge (usually between the ages of two and three), the pediatric dentist may coat them with dental sealant. This sealant covers the hard-to-reach fissures on the molars, sealing out bacteria, food particles, and acid. Dental sealant may last for many months or many years, depending on the oral habits of the child. Dental sealant is an important tool in the fight against tooth decay.
How can I help at home?
Though most parents primarily think of brushing and flossing when they hear the words “oral care,” good preventative care includes many more factors, such as:
Diet
– Parents should provide children with a nourishing, well-balanced diet. Very sugary diets should be modified and continuous snacking should be discouraged. Oral bacteria ingest leftover sugar particles in the child’s mouth after each helping of food, emitting harmful acids that erode tooth enamel, gum tissue, and bone. Space out snacks when possible, and provide the child with non-sugary alternatives like celery sticks, carrot sticks, and low-fat yogurt.
Oral habits
– Though pacifier use and thumb sucking generally cease over time, both can cause the teeth to misalign. If the child must use a pacifier, choose an “orthodontically” correct model. This will minimize the risk of developmental problems like narrow roof arches and crowding. The pediatric dentist can suggest a strategy (or provide a dental appliance) for thumb sucking cessation.
General oral hygiene
– Sometimes, parents clean pacifiers and teething toys by sucking on them. Parents may also share eating utensils with the child. By performing these acts, parents transfer harmful oral bacteria to their child, increasing the risk of early cavities and tooth decay. Instead, rinse toys and pacifiers with warm water, and avoid spoon-sharing whenever possible.
Sippy cup use
– Sippy cups are an excellent transitional aid when transferring from a baby bottle to an adult drinking glass. However, sippy cups filled with milk, breast milk, soda, juice, and sweetened water cause small amounts of sugary fluid to continually swill around young teeth – meaning acid continually attacks tooth enamel. Sippy cup use should be terminated between the ages of twelve and fourteen months or as soon as the child has the motor skills to hold a drinking glass.
Brushing
– Children’s teeth should be brushed a minimum of two times per day using a soft-bristled brush and a pea-sized amount of toothpaste. Parents should help with the brushing process until the child reaches the age of seven and is capable of reaching all areas of the mouth. Parents should always opt for ADA approved toothpaste (non-fluoridated before the age of two, and fluoridated thereafter). For babies, parents should rub the gum area with a clean cloth after each feeding.
Flossing
– Cavities and tooth decay form more easily between teeth. Therefore, the child is at risk for between-teeth cavities wherever two teeth grow adjacent to each other. The pediatric dentist can help demonstrate correct head positioning during the flossing process and suggest tips for making flossing more fun!
Fluoride
– Fluoride helps prevent mineral loss and simultaneously promotes the remineralization of tooth enamel. Too much fluoride can result in fluorosis, a condition where white specks appear on the permanent teeth, and too little can result in tooth decay. It is important to get the fluoride balance correct. The pediatric dentist can evaluate how much the child is currently receiving and prescribe supplements if necessary.

Eruption of Your Child’s Teeth
The eruption of primary teeth (also known as deciduous or baby teeth) follows a similar developmental timeline for most children. A full set of primary teeth begins to grow beneath the gums during the fourth month of pregnancy. For this reason, a nourishing prenatal diet is of paramount importance to the infant’s teeth, gums, and bones.
Generally, the first primary tooth breaks through the gums between the ages of six months and one year. By the age of three years old most children have a “full” set of twenty primary teeth. The American Dental Association (ADA) encourages parents to make a “well-baby” appointment with a pediatric dentist approximately six months after the first tooth emerges. Pediatric dentists communicate with parents and children about prevention strategies, emphasizing the importance of a sound, “no tears” daily home care plan.
Although primary teeth are deciduous, they facilitate speech production, proper jaw development, good chewing habits, and the proper spacing and alignment of adult teeth. Caring properly for primary teeth helps defend against painful tooth decay, premature tooth loss, malnutrition, and childhood periodontal disease.
In what order do primary teeth emerge?
As a general rule-of-thumb, the first teeth to emerge are the central incisors (very front teeth) on the lower and upper jaws (6-12 months). These (and any other primary teeth) can be cleaned gently with a soft, clean cloth to reduce the risk of bacterial infection. The central incisors are the first teeth to be lost, usually between 6 and 7 years of age.
Next, the lateral incisors (immediately adjacent to the central incisors) emerge on the upper and lower jaws (9-16 months). These teeth are lost next, usually between 7 and 8 years of age. First molars, the large flat teeth towards the rear of the mouth, then emerge on the upper and lower jaws (13-19 months). The eruption of molars can be painful. Clean fingers, cool gauzes, and teething rings are all useful in soothing discomfort and soreness. First molars are generally lost between 9 and 11 years of age.
Canine (cuspid) teeth then tend to emerge on the upper and lower jaws (16-23 months). Canine teeth can be found next to the lateral incisors and are lost during preadolescence (10-12 years old). Finally, second molars complete the primary set on the lower and upper jaw (23-33 months). Second molars can be found at the very back of the mouth and are lost between the ages of 10 and 12 years old.
What else is known about primary teeth?
Though each child is unique, baby girls generally have a head start on baby boys when it comes to primary tooth eruption. Lower teeth usually erupt before opposing upper teeth in both sexes.
Teeth usually erupt in pairs – meaning that there may be months with no new activity and months where two or more teeth emerge at once. Due to smaller jaw size, primary teeth are smaller than permanent teeth and appear to have a whiter tone. Finally, an interesting mixture of primary and permanent teeth is the norm for most school-age children.

What’s the Best Toothpaste for My Child?
Evaluating the many brands of oral products claiming to be “best for children” can be an overwhelming task. Selecting an appropriately sized toothbrush and a nourishing, cleansing brand of children’s toothpaste is of paramount importance for maintaining excellent oral health.
Why brush primary teeth?
The importance of maintaining the health of primary (baby) teeth is often understated. Primary teeth are essential for speech production, chewing, jaw development, and they also facilitate the proper alignment and spacing of permanent adult teeth. Brushing primary teeth prevents bad breath and tooth decay, and also removes the plaque bacteria associated with childhood periodontal disease.
What differences are there among toothpaste brands?
Though all toothpastes are not created equal, most brands generally contain abrasive ingredients to remove stains, soapy ingredients to eliminate plaque, fluorides to strengthen tooth enamel, and some type of pleasant-tasting flavoring.
The major differences between brands are the thickness of the paste, the level of fluoride content, and the type of flavoring. Although fluoride strengthens enamel and repels plaque bacteria, too much of it can actually harm young teeth – a condition known as dental fluorosis. Children between the ages of one and four years old are most at risk for this condition, so fluoride levels should be carefully monitored during this time.
Be aware that adult and non-ADA approved brands of toothpaste often contain harsher abrasives, which remove tooth enamel and weaken primary teeth. In addition, some popular toothpaste brands contain sodium lauryl sulfate (shown as “SLS” on the package), which cause painful mouth ulcers in some children.
So which toothpaste brand should I choose?
The most important considerations to make before implementing an oral care plan and choosing a toothpaste brand is the age of the child. Home oral care should begin before the emergence of the first tooth. A cool clean cloth should be gently rubbed along the gums after feeding to remove food particles and bacteria.
Prior to the age of two, the child will have many teeth and brushing should begin. Initially, select fluoride-free “baby” toothpaste and softly brush the teeth twice per day. Flavoring is largely unimportant, so the child can play an integral role in choosing whatever type of toothpaste tastes most pleasant.
Between the middle and the end of the third year, select an American Dental Association (ADA) accepted brand of toothpaste containing fluoride. The ADA logo is clear and present on toothpaste packaging, so be sure to check for it. Use only a tiny pea or rice-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste, and encourage the child to spit out the excess after brushing. Eliminating the toothpaste takes practice, patience, and motivation – especially if the child finds the flavoring tasty. If the child does ingest tiny amounts of toothpaste, don’t worry; this is perfectly normal and will cease with time and encouragement.
Dental fluorosis is not a risk factor for children over the age of eight, but an ADA accepted toothpaste is always the recommended choice for children of any age.
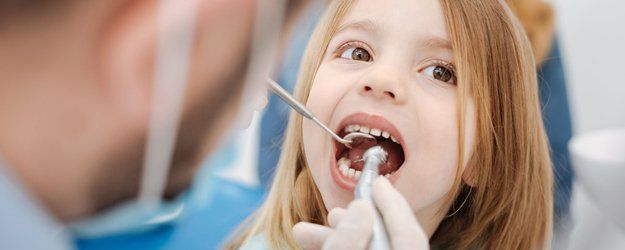
When Should Children Have Their First Dental Visit?
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) suggests that parents should make an initial “well-baby” appointment with a pediatric dentist approximately six months after the emergence of the first tooth, or no later than the child’s first birthday.
Although this may seem surprisingly early, the incidence of infant and toddler tooth decay has been rising in recent years. Tooth decay and early cavities can be exceptionally painful if they are not attended to immediately, and can also set the scene for poor oral health in later childhood.
The pediatric dentist is a specialist in child psychology and child behavior and should be viewed as an important source of information, help, and guidance. Oftentimes, the pediatric dentist can provide strategies for eliminating unwanted oral habits (for example, pacifier use and thumb sucking) and can also help parents in establishing a sound daily oral routine for the child.
What potential dental problems can babies experience?
A baby is at risk for tooth decay as soon as the first tooth emerges. During the first visit, the pediatric dentist will help parents implement a preventative strategy to protect the teeth from harm, and also demonstrate how infant teeth should be brushed and flossed.
In particular, infants who drink breast milk, juice, baby formula, soda, or sweetened water from a baby bottle or sippy cup are at high-risk for early childhood caries (cavities). To counteract this threat, the pediatric dentist discourages parents from filling cups with sugary fluids, dipping pacifiers in honey, and transmitting oral bacteria to the child via shared spoons and/or cleaning pacifiers in their own mouths.
Importantly, the pediatric dentist can also assess and balance the infant’s fluoride intake. Too much fluoride ingestion between the ages of one and four years old may lead to a condition known as fluorosis in later childhood. Conversely, too little fluoride may render young tooth enamel susceptible to tooth decay.
What happens during the first visit?
Pediatric dentists have fun-filled, stimulating dental offices. All dental personnel are fully trained to communicate with infants and young children.
During the initial visit, the pediatric dentist will advise parents to implement a good oral care routine, ask questions about the child’s oral habits, and examine the child’s emerging teeth. The pediatric dentist and parent sit knee-to-knee for this examination to enable the child to view the parent at all times. If the infant’s teeth appear stained, the dentist may clean them. Oftentimes, a topical fluoride treatment will be applied to the teeth after this cleaning.
What questions may the pediatric dentist ask during the first visit?
The pediatric dentist will ask questions about current oral care, diet, the general health of the child, the child’s oral habits, and the child’s current fluoride intake.
Once answers to these questions have been established, the pediatric dentist can advise parents on the following issues:
- Accident prevention
- Adding xylitol and fluoride to the infant’s diet
- Choosing an ADA-approved, non-fluoridated brand of toothpaste for the infant
- Choosing an appropriate toothbrush
- Choosing an orthodontically correct pacifier
- Correct positioning of the head during tooth brushing
- Easing the transition from sippy cup to adult-sized drinking glasses (12-14 months)
- Eliminating fussing during the oral care routine
- Establishing a drink-free bedtime routine
- Maintaining good dietary habits
- Minimizing the risk of tooth decay
- Reducing sugar and carbohydrate intake
- Teething and developmental milestones
If you have further questions or concerns about the timing or nature of your child’s first oral checkup, please ask your pediatric dentist.

How Often Should Children Have Dental Checkups?
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentists (AAPD) advises parents to make biannual dental appointments for children, beginning approximately six months after the first tooth emerges.
These two important yearly visits allow the pediatric dentist to monitor new developments in the child’s mouth, evaluate changes in the condition of teeth and gums, and continue to advise parents on good oral care strategies.
The pediatric dentist may schedule additional visits for children who are particularly susceptible to tooth decay or who show early signs of orthodontic problems.
What is the purpose of dental checkups?
First, the pediatric dentist aims to provide a “good dental home” for the child. If a dental emergency does arise, parents can take the child for treatment at a familiar, comfortable location.
Second, the pediatric dentist keeps meticulous records of the child’s ongoing dental health and jaw development. In general, painful dental conditions do not arise overnight. If the pediatric dentist understands the child’s dental health history, it becomes easier to anticipate future issues and intervene before they arise.
Third, the pediatric dentist is able to educate parents and children during the visit. Sometimes the pediatric dentist wants to introduce one or several factors to enhance tooth health - for example, sealants, fluoride supplements, or xylitol. Other times, the pediatric dentist asks parents to change the child’s dietary or oral behavior - for example, reducing sugar in the child’s diet, removing an intraoral piercing, or even transitioning the child from sippy cups to adult-sized drinking glasses.
Finally, dental X-rays are often the only way to identify tiny cavities in primary (baby) teeth. Though the child may not be feeling any pain, left unchecked, these tiny cavities can rapidly turn into large cavities, tooth decay, and eventually, childhood periodontal disease. Dental X-rays are only used when the pediatric dentist suspects cavities or orthodontic irregularities.
Are checkups necessary if my child has healthy teeth?
The condition of a child’s teeth can change fairly rapidly. Even if the child’s teeth were evaluated as healthy just six months prior, changes in diet or oral habits (for example, thumb sucking) can quickly render them vulnerable to decay or misalignment.
In addition to visual examinations, the pediatric dentist provides thorough dental cleanings during each visit. These cleanings eradicate the plaque and debris that can build up between teeth and in other hard to reach places. Though a good home care routine is especially important, these professional cleanings provide an additional tool to keep smiles healthy.
The pediatric dentist is also able to monitor the child’s fluoride levels during routine visits. Oftentimes, a topical fluoride gel or varnish is applied to teeth after the cleaning. Topical fluoride remineralizes the teeth and staunches mineral loss, protecting tooth enamel from oral acid attacks. Some children are also given take-home fluoride supplements (especially those residing in areas where fluoride is not routinely added to the community water supply).
Finally, the pediatric dentist may apply dental sealants to the child’s back teeth (molars). This impenetrable liquid plastic substance is brushed onto the molars to seal out harmful debris, bacteria, and acid.
If you have questions or concerns about when to schedule your child’s dental checkups please contact your pediatric dentist.
Accepting New Patients
Call 763-263-3262
for an appointment
Corner Oaks Family Dental
290 Eagle Lake Road N
Big Lake, MN 55309

